3phase liquid-liquid-solid separation decanter centrifuge
--------------------------------------------------------------------------


3phase liquid-liquid-solid Decanter centrifuges, also called tricanter , Taking advantage of the principle that the heavy liquid,light liquid and solid phase, with different density and mutually insoluble in the mixed liquid, gain different sedimentation speed in the centrifugal force field or gravity force field, separating stratification or causing the solid particles in the liquid to deposit can be achieved.It is the popular machine throughout the world and widely used in the fish oil,palm oil,kitchen waste oil separation etc.

Separation principle:
The decanter is driven by two motors. The main motor drives the bowl and the housing of differential mechanism to rotate through belt, while the auxiliary motor drives through the belt pulley the input shaft of the differential mechanism to rotate, which, after speed change, drives the helical to rotate. In this way the bowl and helical rotate in the same direction but with certain differential speed.
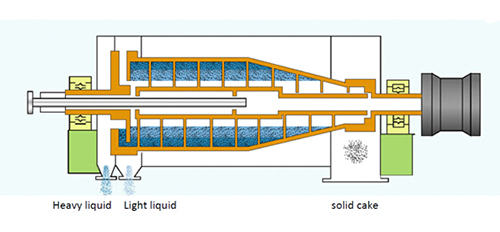
When the material to be processed (blended liquid consisting of solid phase and liquid phase) enters the inner cavity of the helical propeller through feeding pipe, after being accelerated by the two-way conical accelerator, it flows out of the material outlet, and flows into the bowl wall through inner cloth cylinder. The light, heavy and residue phases that make up the suspending liquid, under the action of different centrifugal force, the residue phase quickly subsides onto the inner wall of the bowl, and the heavy phase adheres close to the surface of the residue phase rather slowly, while the light phase adheres close to the surface of the heavy phase rather slowly, forming a dividing plane between the two phases. As the sedimentation of heavy phase increases, the top end of helical blade enters into the sedimentation layer of heavy phase. At this time the bowl and helical propeller are rotating in the same direction at high speed and with a certain difference in speed. This relative difference in rotation speed enables the helical to propel heavy phase particles to move toward the material outlet at the small end, whereas the light phase, through the helical passage, flows toward the liquid phase outlet at the large end, and flows out through the overflow plate with different R values.
Structure:
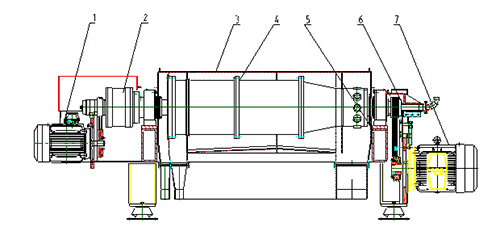
1. Auxiliary motor 2. Gear box 3. Hood 4. Bowl and bearing block 5. base 6. Feed pipe 7. Main motor
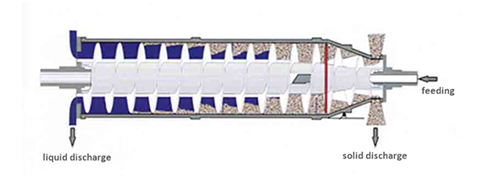
Compared with 2-phase decanter:
|
Model
|
Diameter
(mm)
|
Speed (rpm)
|
Length
(mm)
|
G-force
|
Capacity
(m3/h)
|
Main motor Power
(kw)
|
Assistant motor power
(kw)
|
Weight
(kg)
|
Overall Size
(L × W × H)
(mm)
|
|
PDCS-17
|
420
|
3300
|
1680
|
2550
|
5~20
|
30
|
11
|
3610
|
3331 × 990 × 1066
|
|
PDCS-18
|
450
|
3300
|
2000
|
2739
|
4~50
|
30
|
11
|
3655
|
4000 × 1120 × 1239
|
|
PDCS-20
|
500
|
3200
|
2000
|
2860
|
5~45
|
55
|
11
|
4213
|
4489 × 1160 × 1350
|
|
PDCS-21
|
540
|
2800
|
2000
|
2366
|
5~50
|
45
|
15
|
5290
|
4587 × 1285 × 1368
|

--------------------------------------------------------------------------
Update:2014-11-26 13:00:17 Visits: Category:3phase tricanter
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
